| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
- 참조형변수
- 컬렉션프레임워크
- 한국건설관리시스템
- abstract
- 제네릭
- 사용자예외클래스생성
- cursor문
- 컬렉션 타입
- oracle
- 메소드오버로딩
- 생성자오버로드
- EnhancedFor
- exception
- 정수형타입
- GRANT VIEW
- 오라클
- 환경설정
- 자바
- 자동차수리시스템
- 다형성
- 어윈 사용법
- 추상메서드
- NestedFor
- 집합_SET
- 대덕인재개발원
- 예외처리
- 인터페이스
- Java
- 예외미루기
- 객체 비교
- Today
- Total
거니의 velog
230714 자바 강의 본문
[Triangle.java]
package ddit.chap05.sec04;
public class Triangle {
// 객체 배열
// 배열의 시작 주소를 p가 가지게 함.
private Point[] p; // 배열만 선언. 객체는 아직 생성되지 않음.
// 배열 안에 3개의 Point 객체 주소를 포함시킴.
// 이중 포인터 구조.
Triangle(Point[] p) {
this.p = new Point[] {new Point(100, 100),
new Point(500, 100),
new Point(250, 250)};
}
public void draw() {
System.out.println(p[0] + "과 " + p[1] + "을(를) 연결합니다.");
System.out.println(p[1] + "과 " + p[2] + "을(를) 연결합니다.");
System.out.println(p[2] + "과 " + p[0] + "을(를) 연결합니다.");
}
}[ShapeExample.java]
package ddit.chap05.sec04;
public class ShapeExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Triangle t1 = new Triangle(new Point[3]);
t1.draw(); // Point 클래스에서 toString() 메서드를 오버라이딩(재정의)하여 내용을 출력.
/*
* (100, 100)과 (500, 100)을(를) 연결합니다.
* (500, 100)과 (250, 250)을(를) 연결합니다.
* (250, 250)과 (100, 100)을(를) 연결합니다.
*/
}
}[1차원 배열]
타입명[ ] 배열명 = new 타입명[크기];
int[ ] score = new int[5];
[2차원 배열, 다차원 배열]
타입명[ ][ ] 배열명 <- 제일 많이 쓰는 타입
타입명 배열명[ ][ ]
타입명[ ] 배열명[ ]
테이블 구조를 이룸.
행 -> 튜플.
열 -> 컬럼.
타입명[ ][ ] 배열명 = new 타입명[행-크기][열-크기];
5명의 3과목 점수를 테이블로 표시? 5행 3열
int[ ][ ] score = new int[5][3];
int[ ] score = new int[5]; -> 행이 5개로 고정됨.
score[0] = new int[3]; -> 열이 3개로 고정됨.
score[1] = new int[3]; -> 열이 3개로 고정됨.
score[2] = new int[3]; -> 열이 3개로 고정됨.
score[3] = new int[3]; -> 열이 3개로 고정됨.
score[4] = new int[3]; -> 열이 3개로 고정됨.
배열 안의 배열(Array in Array).
int[ ][ ] score = new int[5][ ]; - 가변길이배열 (Jagged Array)
int[ ] score = new int[5];
score[0] = new int[4]; -> 열이 4개로 고정됨.
score[1] = new int[2]; -> 열이 2개로 고정됨.
score[2] = new int[3]; -> 열이 3개로 고정됨.
score[3] = new int[4]; -> 열이 4개로 고정됨.
score[4] = new int[5]; -> 열이 5개로 고정됨.
int[ ][ ] score = { { 0행 } , { 1행 } , { 2행 } , { 3행 } , { 4행 } };
int[ ][ ] score = { { 10,20,30 } , { 90,80,70 } , { 40,20,30 } , { 90,80,70 } , { 30,40,50 } };
| 10 – 0행 0열 | 20 – 0행 1열 | 30 – 0행 2열 |
| 90 – 1행 0열 | 80– 1행 1열 | 70– 1행 1열 |
| 40 | 20 | 30 |
| 90 | 80 | 70 |
| 30 | 40 | 50 |
2차원 배열의 배열명.length?
score.length = 2; -> 행의 개수
열의 개수를 알고 싶다면?
각행.length;
score[0].length; = 3;
score[1].length; = 3;
score[2].length; = 3;
score[3].length; = 3;
score[4].length; = 3;
[TwoDimensionArrayExample.java]
package ddit.chap05.sec05;
// 5명의 3과목 성적이 다음과 같다. 이를 배열에 저장하고 출력하시오.
// [데이터]
/* 국어 영어 수학
* 75 80 65
* 95 85 85
* 65 85 85
* 90 60 85
* 95 90 95
*/
public class TwoDimensionArrayExample {
static int[][] score; // 배열명 선언.
static String[] name;
public static void main(String[] args) {
twoDimMethod01();
printScore();
}
public static void twoDimMethod01() {
// 데이터 입력
score = new int[][] {{75,80,65,0,0,1},
{95,85,85,0,0,1},
{65,85,85,0,0,1},
{90,60,85,0,0,1},
{95,90,95,0,0,1}}; // 가변형 배열로 선언.
name = new String[] {"홍길동", "이순신", "김상훈", "이성계", "강감찬"};
sumAvg();
getRank();
}
public static void printScore() {
// 데이터 출력
// 바깥쪽 for는 행을, 안쪽 for는 열을 담당.
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
System.out.println("이 름 국어 영어 수학 총점 평균 등수");
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
for(int i=0; i<score.length; i++) { // 행
System.out.print(name[i] + " ");
for(int j=0; j<score[i].length; j++) { // 열
System.out.printf("%5d", score[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void sumAvg() {
// 총점, 평균 구하기
for(int i=0; i<score.length; i++) { // 행
for(int j=0; j<3; j++) { // 열
score[i][3] += score[i][j]; // 총점
}
score[i][4] = score[i][3] / 3; // 평균
}
}
public static void getRank() {
// 등수 구하기
for(int i=0; i<score.length; i++) { // 기준값 위치
for(int j=0; j<score.length; j++) { // 비교값 위치
if(score[i][3] < score[j][3]) score[i][5]++;
}
}
}
}
[ArrayCopyExample.java]
package ddit.chap05.sec06;
import java.util.Arrays;
// 배열 복사 - 옅은 복사(shadow copy, 주소값만 복사), 주소값을 공유(call by reference, address)하므로 값의 변경이 동시에 일어난다(부작용, side effect).
// int[] num = new int[4];
// int[] su = num;
// 주로 매개변수로 넘겨줄 때 많이 활용.
// public void abc() {
// int[] num = new int[4];
// System.out.println(su[2]); // 10
// }
// public void kbs(int[] su) {
// su[2] = 10;
// }
//////////////////////////////////////////////
// 깊은 복사(deep copy)
/* - 배열이 별도로 생성되어 원본 배열의 값을 복사.
* - for문 이용(수동 복사)
* - Object 클래스 제공, clone();
* - System 클래스 제공, arraycopy();
*/
public class ArrayCopyExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
forCopy();
cloneCopy();
arrayCopy();
}
public static void forCopy() {
int[] source = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
int[] target = new int[source.length];
for(int i=0; i<source.length; i++) {
target[i] = source[i];
}
target[1] = 9000;
System.out.println(source); // [I@32d992b2
System.out.println(target); // [I@215be6bb. 서로 다른 주소 값을 가리키므로 서로 영향을 주지 않는다.
System.out.println("source : " + Arrays.toString(source)); // source : [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
System.out.println("target : " + Arrays.toString(target)); // target : [10, 9000, 30, 40, 50]
}
public static void cloneCopy() {
int[] source = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
int[] target = source.clone(); // 반환 타입 : 배열. 변수 타입도 배열로 맞춰줘야 한다.
target[2] = 5000;
System.out.println(source); // [I@4439f31e
System.out.println(target); // [I@5dfcfece. 서로 다른 주소 값을 가리키므로 서로 영향을 주지 않는다.
System.out.println("source : " + Arrays.toString(source)); // source : [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
System.out.println("target : " + Arrays.toString(target)); // target : [10, 20, 5000, 40, 50]
}
public static void arrayCopy() {
int[] source = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
// System.arraycopy(src, srcPos, dest, destPos, length);
/* src : 원본 배열명
* srcPos : 원본 배열에서 복사해줄 위치
* dest : 복사받을 배열명
* destPos : 복사받을 배열 위치
* length : 복사해 줄 배열요소의 숫자
*/
int[] target = new int[10];
System.arraycopy(source, 0, target, 4, source.length);
System.out.println(source); // [I@23ceabc1
System.out.println(target); // [I@5d5eef3d. 서로 다른 주소 값을 가리키므로 서로 영향을 주지 않는다.
System.out.println("source : " + Arrays.toString(source)); // source : [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
System.out.println("target : " + Arrays.toString(target)); // target : [0, 0, 0, 0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 0]
}
}[ArrayConversionEx.java]
package ddit.chap05.sec07;
import java.util.Random;
public class ArrayConversionEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayConversion ac = new ArrayConversion();
ac.histogram();
ac.conversion();
}
}
class ArrayConversion {
private int[] dice = new int[6];
private Random random = new Random();
public ArrayConversion() {
for(int i=0; i<50; i++) {
// random class의 nextInt() : 정수형 난수 하나 발생.
// nextInt(n) : 0 ~ (n-1) 사이의 정수형 난수 1개 발생.
int rand = random.nextInt(6)+1; // 1~6 사이의 난수 발생.
dice[rand-1]++; // 발생된 횟수를 1씩 증가.
}
}
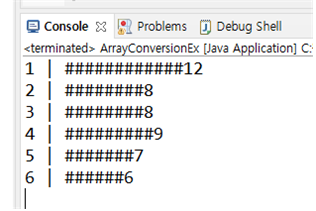
public void histogram() {
for(int i=0; i<dice.length; i++) {
System.out.print((i+1)+" | ");
for(int j=0; j<dice[i]; j++) {
System.out.print("#");
}
System.out.println(dice[i]);
}
}
public int getMaxNum() {
int rowCnt = dice[0]; // 임시최대값(행의 수)
for(int i=1; i<dice.length; i++) {
if(rowCnt < dice[i]) {
rowCnt = dice[i];
}
}
return rowCnt;
}
public void conversion() {
int r = getMaxNum(); // 행의 수
char[][] histo = new char[r][6];
for(int i=0; i<dice.length; i++) { // 열(6개)
for(int j=0; j<dice[i]; j++) { // 행
histo[j][i] = '#';
}
}
}
}
'대덕인재개발원 > 대덕인재개발원_Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 230718 자바 강의 (0) | 2023.07.18 |
|---|---|
| 230717 자바 강의 (0) | 2023.07.17 |
| 230713 자바 강의 (0) | 2023.07.13 |
| 230712 자바 강의 (0) | 2023.07.12 |
| 230711 자바 강의 (0) | 2023.07.12 |




