Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 | 31 |
Tags
- exception
- 사용자예외클래스생성
- cursor문
- 환경설정
- NestedFor
- 오라클
- 인터페이스
- EnhancedFor
- 예외처리
- GRANT VIEW
- 집합_SET
- 자바
- 어윈 사용법
- abstract
- 다형성
- 객체 비교
- 제네릭
- 예외미루기
- 한국건설관리시스템
- 대덕인재개발원
- 참조형변수
- Java
- oracle
- 메소드오버로딩
- 자동차수리시스템
- 추상메서드
- 정수형타입
- 생성자오버로드
- 컬렉션 타입
- 컬렉션프레임워크
Archives
- Today
- Total
거니의 velog
230731 자바 강의 본문
[ExceptionExample02.java]
package ddit.chap10.sec01;
public class ExceptionExample02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
exceptionMethod01(); // at ddit.chap10.sec01.ExceptionExample02.main(ExceptionExample02.java:7)
}
public static void exceptionMethod01() {
// 1/5 + 1/4 + 1/3 + 1/2 ...
double sum = 0;
try {
// 강요하는 예외
// 사용자가 선택하는 예외 : Runtime Exception
// for(int i=5; i>=0; i--) { // 오류
for(int i=5; i>0; i--) { // 정상 작동.
sum += (1/i); // 오류 위치. 이후의 코드는 실행되지 않는다. // at ddit.chap10.sec01.ExceptionExample02.exceptionMethod01(ExceptionExample02.java:19)
}
System.out.println("합 = " + sum);
}catch(ArithmeticException e) { // java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero => 산술논리연산 오류. 원인 : 0으로 나누어지는 오류 발생
e.printStackTrace(); // call stack 메모리에 있는 오류 메시지를 그대로 출력.
}catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("예외발생");
System.out.println(e.getMessage()); // printStackTrace()와 거의 유사한 내용. / by zero 만 출력해 준다.
}finally {
System.out.println("예외처리 종료");
}
}
}

[예외를 미루는 방법]
[ExceptionExample03.java]
package ddit.chap10.sec01;
public class ExceptionExample03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExceptionExample03 ex03 = new ExceptionExample03();
try { // 예외를 미룬 메서드에서 정의한 모든 예외클래스를 정의해야 하며, 범위를 좁힐 수 없다=>throws에 예외처리한 갯수만큼 정의해야 한다.
// System.in.read();
ex03.sample();
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace(); // java.lang.NullPointerException
// System.out.println(e.getMessage()); // null
}
}
public void sample() throws Exception {
// throws 뒤에 2개의 예외 클래스(NullPointerException, Exception)를 선언하여 메서드를 부르는 쪽에서 예외 처리를 하도록 미룬다. 수익자 부담 원칙.
// throws 뒤에 나오는 예외를 조심하라는 경고.
// 예외의 종류를 짐작할 수 없다면 Exception만 써도 된다.
// throws는 sample() 메서드를 호출하는 곳에서 try~catch 처리를 해야 함. 강요된 Exception 이라고도 한다.
Person1 p1=null;
System.out.println("[회원정보]");
System.out.println(p1.toString()); // Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException
}
}
class Person1 {
int age;
String name;
Person1() {}
Person1(int age, String name) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "이름 : " + name + ", 나이 : " + age;
}
}
[ExceptionExample04.java]
package ddit.chap10.sec01;
// 사용자 예외 클래스 생성
// 사용형식
// default 이상 접근 지정자 사용. 싱글톤 패턴 사용 잘 안함.
// 접근지정자 class 예외클래스명 extends Exception|RuntimeException{ // 강요되어진 예외.
// 예외클래스명(String message){ // 예외가 발생되었을 때 원인으로 표출될 메시지.
// super(message);
// }
// }
// ** 예외클래스 호출?
// throw 예외클래스 객체명
// ex) throw new Exception(); 예외가 없더라도 반드시 예외를 발생시킴.
public class ExceptionExample04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
exceptionSample("genious"); // 별명은 genious 입니다...
exceptionSample("fool"); // Exception in thread "main" ddit.chap10.sec01.MyException: 사용자정의 예외
}catch(MyException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
System.out.println("프로그램 종료."); // commit문 처리 방법 중 하나.
}
public static void exceptionSample(String nickName) throws MyException {
if("fool".equals(nickName)) {
throw new MyException("사용자정의 예외"); // at ddit.chap10.sec01.ExceptionExample04.exceptionSample(ExceptionExample04.java:29)
}
System.out.println("별명은 " + nickName + " 입니다...");
}
}
class MyException extends RuntimeException { // 사용자 정의 예외클래스
private static String msg;
MyException(String msg) {
super(msg);
}
}

OJDBC.jar 파일을 제대로 라이브러리에 추가했는지 찾을 때 사용.
DriverManager 클래스명을 찾을 때 사용.


[ExceptionExample05.java]
package ddit.chap10.sec01;
public class ExceptionExample05 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // 해결방법 2. main() 메서드에 처리. 결국은 예외미루다 미루다 main()에서 발생. 좋은 방법은 아님.
ExceptionExample05 ex05 = new ExceptionExample05();
// try {
// ex05.method01();
// } catch (Exception e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// } // 해결방법 1 - try~catch 문으로 묶기.
ex05.method01();
}
public void method01() throws Exception {
method02();
}
public void method02() throws Exception {
method03();
}
public void method03() throws Exception {
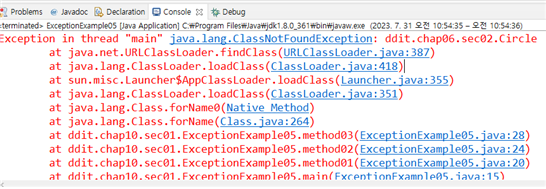
Class c1 = Class.forName("ddit.chap06.sec02.Circle"); // 현재 해당 경로에 클래스가 없는 상태.
}
}

- https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/index.html
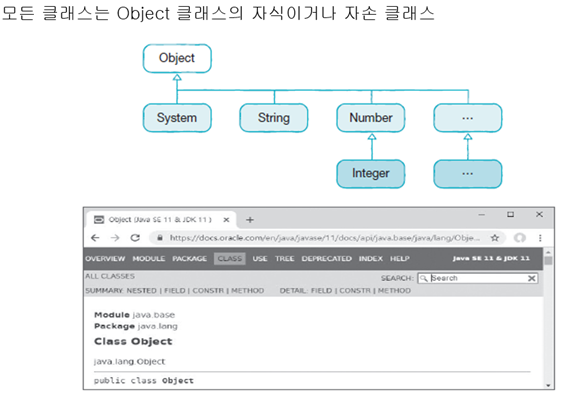
import 필요 없다.
System, String 클래스는 구글링으로 공부.
String : 문자열을 다루는 클래스. 한 번 만들어지면 축소하거나 늘릴 수 없다.
immutable. 배열도 같은 의미.
String buffer, String builder를 더 많이 사용한다.
Number 클래스를 상속받은 래퍼클래스 8가지.

스레드 : 메소드가 보통 스레드. 메인 메서드라고 안하고 메인 스레드라고 부름.
스레드는 고급 자바에서 배울 것.
모든 클래스는 Object를 상속받는다. 어느 클래스나 다 사용 가능.

[ExceptionExample06.java]
package ddit.chap10.sec01;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ExceptionExample06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
int res = System.in.read();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}[ObjectExample01.java]
package ddit.chap11.object;
public class ObjectExample01 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Person p1 = new Person("정몽주");
Person p2 = new Person("정몽주");
// System.out.println("p1 = " + p1); // p1 = ddit.chap11.object.Person@15db9742
// System.out.println("p1 = " + p1.toString()); // p1 = ddit.chap11.object.Person@15db9742
// System.out.println(p1.classInfo()); // ddit.chap11.object.Person@15db9742
System.out.println("p1 = " + p1); // p1 = ddit.chap11.object.Person@15db9742
System.out.println("p2 = " + p2); // p2 = ddit.chap11.object.Person@6d06d69c
if (p1==p2) {
System.out.println("같은 객체");
}else {
System.out.println("다른 객체"); // 다른 객체가 나옴. 객체의 주소값이 다르기 때문에.
}
if (p1.toString().equals(p2.toString())) {
System.out.println("같은 내용");
}else {
System.out.println("다른 내용");
}
}
}
class Person {
String name;
Person(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String classInfo() {
// return getClass().getName(); // ddit.chap11.object.Person
return getClass().getName() + "@" + Integer.toHexString(hashCode());
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return name;
}
}
[ObjectExample02.java]
package ddit.chap11.object;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ObjectExample02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
objectClone();
}
public static void objectClone() {
// 자기 복제
int[] num1 = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
int[] num2 = num1.clone();
System.out.println("num1 = " + Arrays.toString(num1));
System.out.println("num2 = " + Arrays.toString(num2));
Student s1 = new Student("이순신");
// 객체에 clone) 사용하기 위해서는
// 해당 객체의 생성에서 Cloneable 인터페이스를 구현해야 하고,
// clone() 메서드를 재정의(오버라이드)해야 한다.
Student s2 = (Student) s1.clone();
System.out.println("s1 = " + s1); // ddit.chap11.object.Student@15db9742
System.out.println("s2 = " + s2); // ddit.chap11.object.Student@6d06d69c
System.out.println("s1.name = " + s1.name);
System.out.println("s2.name = " + s2.name);
// 주소는 다르나 내용이 같은 경우 : 자기 복제.
if(s1.name.equals(s2.name)) {
// if(s1.name == s2.name) {
System.out.println("같은 내용");
}else {
System.out.println("다른 내용");
}
}
}
class Student implements Cloneable {
String name;
Student(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return name;
}
@Override
public Object clone() {
Object obj = null;
try {
obj = super.clone();
}catch(CloneNotSupportedException e) {}
return obj;
}
}

'대덕인재개발원 > 대덕인재개발원_Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 230802 자바 강의 (0) | 2023.08.02 |
|---|---|
| 230801 자바 강의 (0) | 2023.08.01 |
| 230729 자바 과제 _ 클래스 다이어그램 구현 (0) | 2023.07.29 |
| 230728 자바 강의 (0) | 2023.07.29 |
| 230727 자바 강의 (0) | 2023.07.29 |




